Professor Ronald HayFRS FRSE FMedSci
Chair of Molecular Biology
Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology, School of Life Sciences

Contact
Research
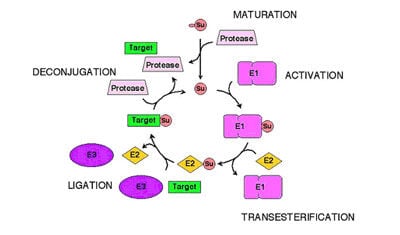
SUMO Conjugation
Our laboratory has established conjugation with the Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) as an important regulatory mechanism in eukaryotes. By analysing the site of modification in a number of proteins we proposed a SUMO consensus modification site consisting of the sequence yKxE, where "y" represents a large hydrophobic amino acid and " x " represents any amino acid (figure 1b). We further demonstrated that this site constitutes a transferable signal that confers the ability to be modified with SUMO on proteins to which it is linked. In chordates there are 3 members of the SUMO family. Although SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 are 97% identical they share only 50% sequence identity with SUMO-1 and appear to be functionally distinct. We demonstrated that in contrast to SUMO-1, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 could form poly-SUMO-2 chains.
Although we reported the existence of these chains in 2001, it is only recently that their function has been revealed. We recognised that the RING domain containing protein Rnf4 also contained multiple SUMO interaction motifs (SIMs) and demonstrated that it could function as a ubiquitin E3 ligase with a unique specificity for polySUMO chains. We further showed that Rnf4 is the ubiquitin ligase responsible for arsenic inducible, proteasomal degradation of the Promyelocytic Leukaemia (PML) protein. In Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia (APL) the PML protein is fused to the Retinoic Acid Receptor and the disease can be effectively treated by arsenic administration. Arsenic induces modification of PML with SUMO and subsequent proteasomal degradation of PML. Our identification of Rnf4 as the E3 ligase responsible for the SUMO-dependent degradation of PML provides the molecular basis for the therapeutic action of a drug currently used to treat leukaemia (Tatham et al., 2008). Subsequent studies on arsenic and PML have established the dynamics and cell biology of this process (Geoffroy et al., 2010; Hattersley et al., 2011). The objective of present work is to determine the signal transduction pathway, activated by arsenic, which leads to increased SUMO modification of PML. X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy are being employed to determine the structure of the ubiquitin E3 ligase Rnf4, bound to its poly SUMO substrate and its cognate E2 conjugating enzyme (Plechanovova et al., 2011,2012).

Stable Isotope Labelling with Amino Acids in Cell culture (SILAC)
In research that is currently underway we are using Stable Isotope Labelling with Amino Acids in Cell culture (SILAC) coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry to carry out quantitative temporal analysis of the SUMO proteome as cells respond to various challenges. To accomplish this we are employing the most up-to-date Q-Exactive mass spectrometer. This is a productive area of research that provides a system wide view of SUMO modification, amenable to mathematical analysis (Golebiowski et al., 2009, Bruderer et al., Tatham et al., 2011). Many further analyses are planned: as cells progress through the cell cycle; exposure of cells to arsenic, DNA damaging agents and cytokines.
Media availability
I am available for media commentary on my research.
Role of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins in transcriptional regulation
Contact Corporate Communications for media enquiries.
Areas of expertise
- Cancer
Second supervisor
PhD opportunity
Awards
| Award | Year |
|---|---|
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Cancer Research UK Programme Award (renewal) | 2023 |
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Wellcome Investigator Award | 2019 |
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Cancer Research UK Programme Award (renewal) | 2016 |
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Wellcome Trust Senior Investigator Award | 2012 |
| National Sciences Prizes awarded since 1990 / The Novartis Medal & Prize of the Biochemical Society | 2012 |
| Fellow of Learned Societies and Colleges / Fellow of Academia Europaea | 2012 |
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Cancer Research UK Programme Award (renewal) | 2011 |
| Fellow of the Royal Society | 2010 |
| Member of the European Molecular Biology Organisation | 2009 |
| Fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences | 2005 |
| Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh | 1996 |
Stories
News
Seven new papers have been published this month in The Biochemical Journal, representing a major collaboration between multiple groups at the Francis Crick Institute in London, University College London and The University of Dundee.
News
A new article from the Lamond group, published in eLife, reports the identification of the plant biflavone, hinokiflavone, as a pre-mRNA splicing modulator (Pawellek et al., 2017).