Location
Fluid Mechanics Laboratory
We have a range of physical modelling and experimental facilities to support research and teaching in fluid mechanics

Fulton Building
DD1 4HR
Opening hours
08:30 – 18:00 Monday – Friday
Accessibility
View accessibility information for the Fulton Building at AccessAble
About
Our bespoke physical modelling and experimental research facilities have been designed for the investigation of a wide range of problems in environmental fluid mechanics, chiefly those associated with offshore, coastal and estuarine environments. We also have apparatus for laboratory-based teaching in fluid mechanics and civil engineering hydraulics.
Surface wave flume
This flume facility is 14 m long x 0.6 m wide x 0.6 m deep with a piston-type wavemaker capable of generating linear and non-linear waves in shallow to deep water.
Applications:
- experiments on wave interactions with wave energy devices, oil and gas platforms, floating wind turbines and floating fish pens

Channel-basin facility
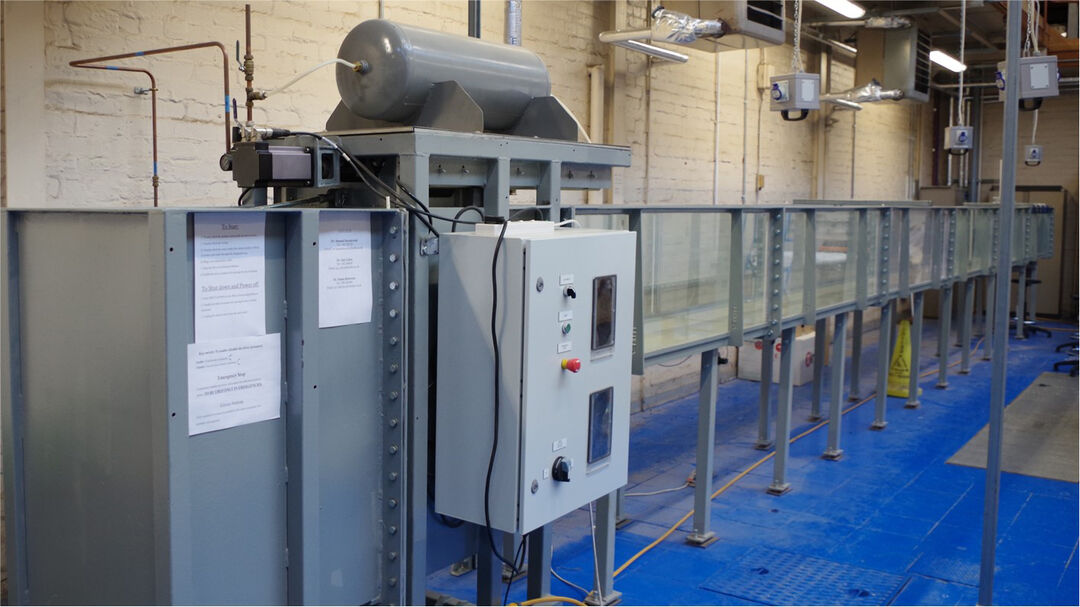
This purpose built facility consists of a 3.2 m long x 0.6 m wide x 1 m deep “estuarine” channel connected to a larger 2 m long x 2 m wide x 1 m deep “sea” basin incorporating a tide generation unit.
Applications:
- experiments on estuarine exchange flows, mixing and circulations
- turbidity currents and their deposits at slope breaks and loss of channel confinement
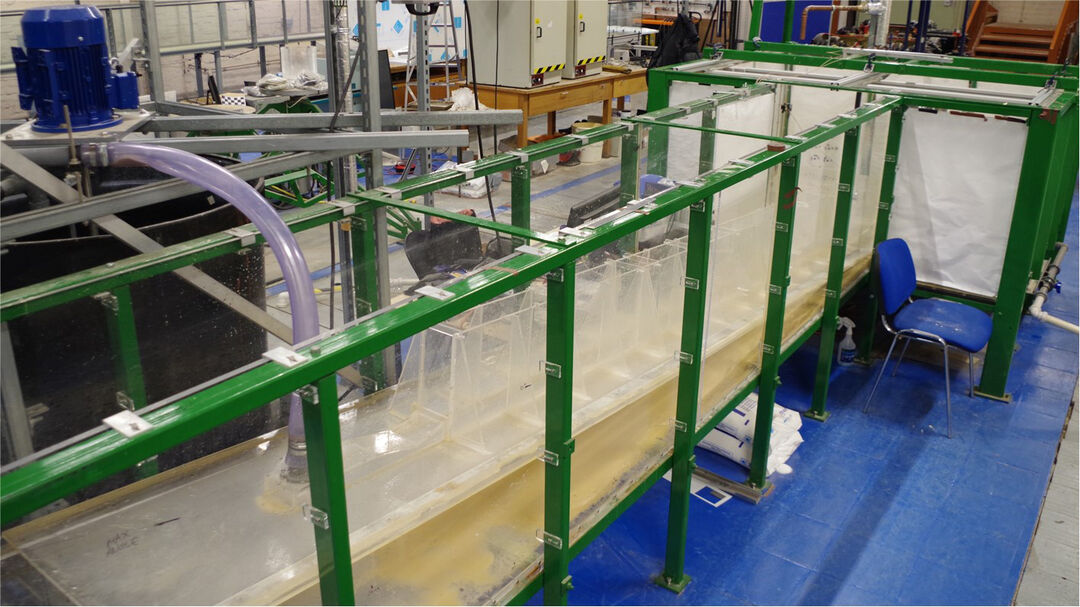

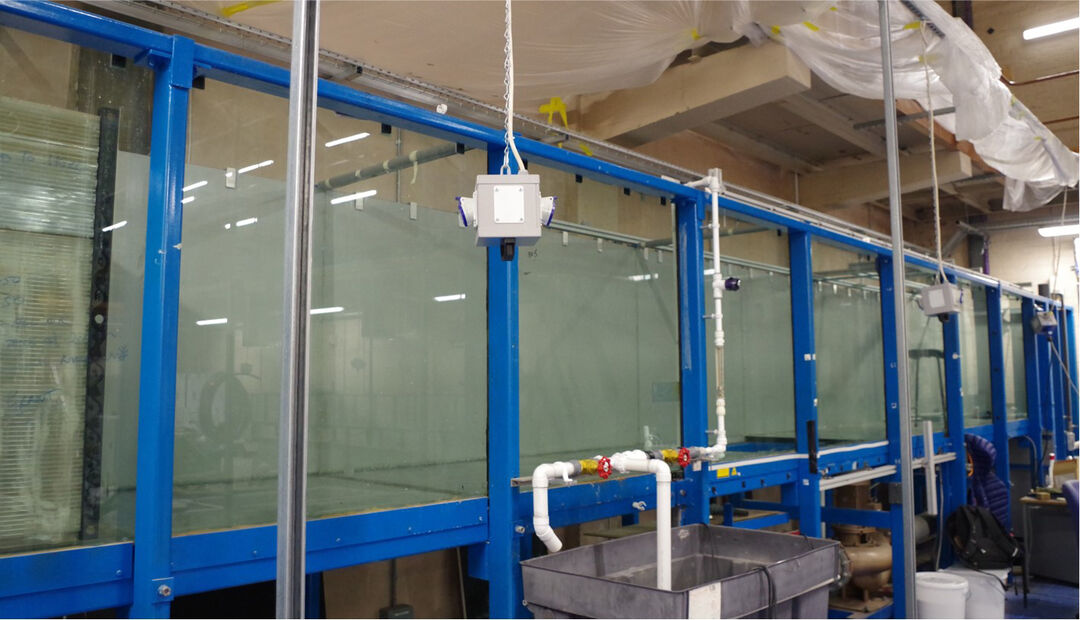
Large recirculating tank facility
This 11 m long glass-walled recirculating facility has a large 1.2 m wide by 1.0 m deep cross-sectional area to permit the study of large-scale environmental fluid mechanics problems.
Applications:
- experiments on particle-laden buoyant jets and plumes in cross-flowing currents
- marine wastewater and desalination discharges
- spreading gravity-driven flows and surface plumes

Grid-array-stirred settling column
This facility was designed and built in-house for the study of cohesive sediment dynamics, including the flocculation, hindered settling and sedimentation of sand-mud mixtures, under controlled grid-generated turbulence.
Applications:
- estuarine and coastal sediment dynamics and morphodynamics
- physical characterisation of the settling, deposition and resuspension of aquaculture particulate wastes
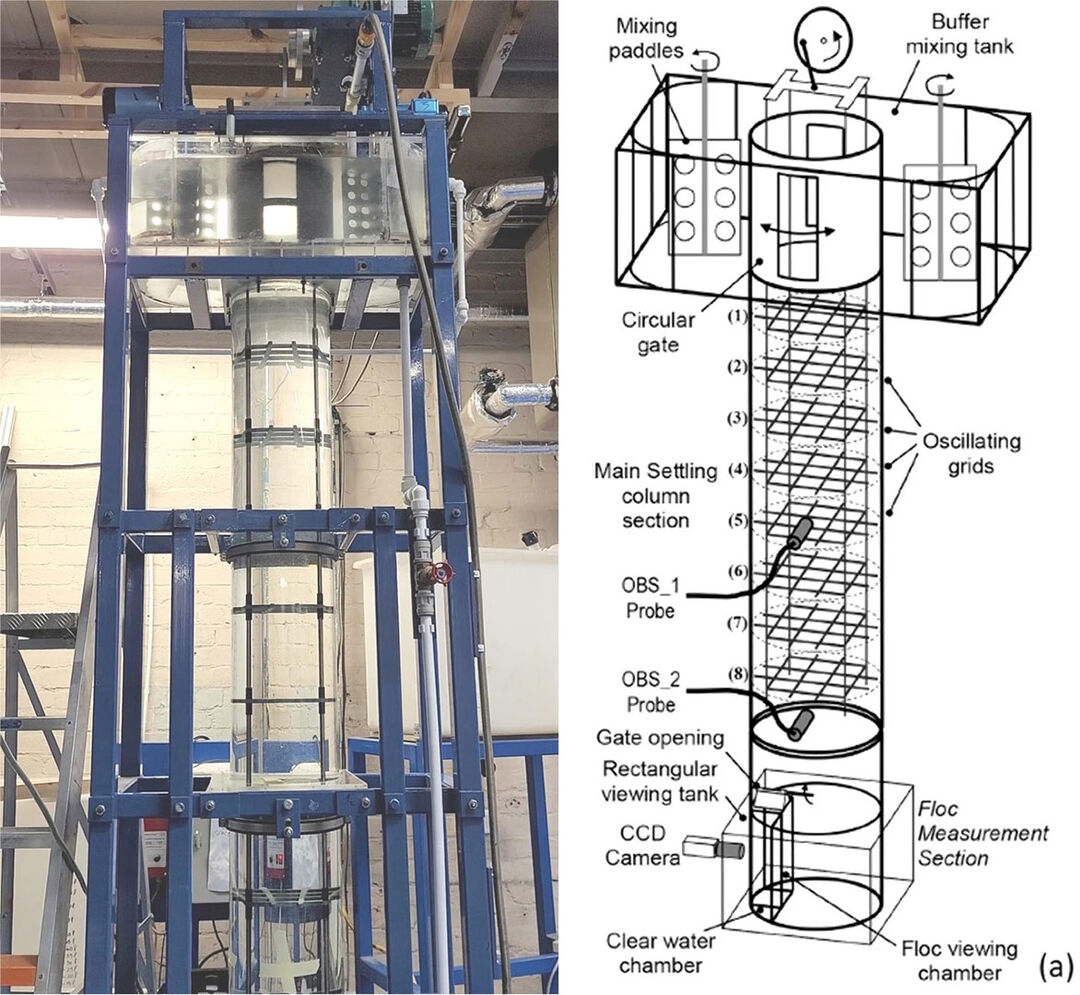
Diagram showing the main components of the grid-array-stirred settling column, including mixing paddles at the top, oscillating grids in the main column and floc measurement section and viewing tank at the bottom.
Rotating tables
We have two bespoke rotating tables for the experimental modelling large-scale geophysical flows where Earth rotation effects are important.
Applications:
- oceanic circulations and mixing, deep water outflows, topographic steering of currents
- fundamental study of rotating flows
Tsunami wave simulator
This flume facility is designed to generate very long surface waves through the subsurface displacement of water, similar to the generation of tsunamis waves by a sudden displacement of the ocean floor.
Applications:
- experimental investigation of wave run-up and backwash on a sloping coastline
Armfield open channel flow flume (teaching)
Undergraduate teaching facility for demonstration of open channel flows over weirs and generation of hydraulic jumps downstream of gates.
Pipe flow apparatus (teaching)
Undergraduate teaching facility for demonstration of energy head loss in pipe flow due to wall friction.
Measurement equipment and simulation
We also have a range of high precision measurement equipment for flow and density fields, as well as a number of computational simulation tools, including:
- 2D particle image velocimetry (PIV) system for flow field measurements
- Acoustic doppler velocimeter (ADV) and ultrasonic velocity profilers (UVP)
- Optical backscatter sensors (OBS) for turbidity and suspended sediment measurements
- Micro-conductivity probes for profiling density structure in stratified flows
- High-resolution cameras for flow visualisation and particle tracking
- Wave pressure gauges for the study of wave-structure interactions
- Specialist numerical modelling and simulation (see High Performance Computing Facility and Computational Modelling)