
Contact
Biography
Henry studied for his undergraduate in Immunology at the University of Glasgow, graduating in 2004. He then completed a PhD on TGF-B homologues from parasites which induce Tregs with Professor Rick Maizels at the University of Edinburgh (graduating in 2008).
Henry then moved Brisbane and Cairns, Australia, to undertake a postdoctoral researcher post with Prof Alex Loukas. He worked on a clinical trial of human hookworm infection, to attempt to treat celiac disease. He returned to Rick Maizels lab in Edinburgh in 2010, working on using parasite secretory products to treat asthma. While there he received an Asthma UK Senior Postdoctoral Fellowship (2013) to continue this work. In 2014 he received a Chancellors Fellowship to set up his own laboratory in Edinburgh.
In 2020 Henry moved his lab to the University of Dundee. The lab’s interests focus on immunomodulation by parasites, and the role of the IL-33 pathway in infection and immunopathology. He is deputy head of the division of Cell Signalling and Immunology.
Research
Plain language research summary
We work on how parasitic worms interact with the immune system, suppressing immune responses against them, and allowing them to survive. We also look at how the immune system can eject parasitic worms, and how we can block parasite suppression of the host immune response, to eject these parasites. Finally, we work on how the factors that parasites release to suppress immune responses could be developed to treat diseases caused by the immune system, including asthma, obesity and fibrosis.
Research summary
Parasitic helminths have co-evolved with their mammalian hosts, resulting in their development of sophisticated methods of immune modulation to allow the parasites to survive despite efforts of the immune response to eject them. Our lab focuses on how parasitic helminths achieve this, identifying factors which modulate the host immune response and characterising their molecular mechanisms of action. By better understanding how helminths modulate the host immune response, we could learn from these sophisticated parasites, and use this knowledge to develop new treatments for immune-mediated diseases such as allergies and asthma. Conversely, by understanding how helminths interact with the immune system, we can understand how to better combat these important pathogens which afflict hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Heligmosomoides polygyrus adult parasites – a nematode worm which infects mice and lives in the small intestine. These parasites can be up to 1 cm long when stretched out, but usually are tightly coiled as shown.
The Hygiene Hypothesis
Parasitic helminth infections negatively correlate with the prevalence of allergic immune disease, and as the prevalence of parasitic infections has decreased (due to improvements in sanitation and hygiene) over the last century, we have suffered and epidemic of allergic disease. Parasites achieve this effect through the release of soluble immunodulatory factors which suppress the parasite-toxic type 2 immune response, and as a “side-effect” suppress allergic immune responses.
We recently characterised two of the factors which the murine intestinal parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus uses to achieve this, both of which act against the IL-33 pathway. HpARI acts against IL-33 (Osbourn, 2017, Immunity), while HpBARI acts against the IL-33 receptor (Vacca, 2020, eLife) as envisaged in the Wormuvian Man diagram, below. IL-33 is also critical in the development of allergic diseases such as asthma, and we are interested in developing these parasite-derived factors as asthma treatments.
The immune modulating activities of H. polygyrus is not limited to IL-33, and we are currently investigating further activities of the parasite against other immune pathways.
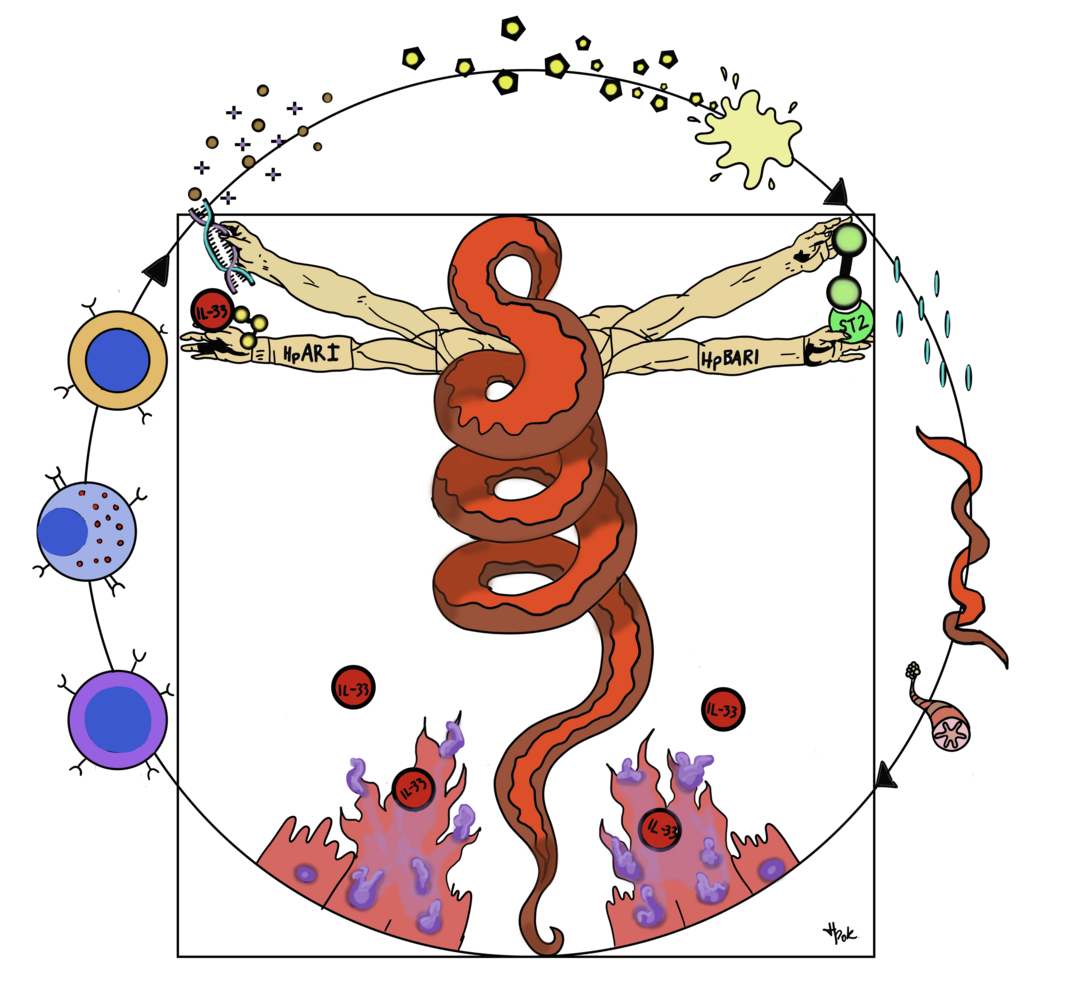
Wormuvian man. This diagram shows the H. polygyrus parasite as Da Vinci’s Vitruvian man, in the centre of the immune responses induced against it. H. polygyrus infection causes necrosis of intestinal epithelial cells, and release of IL-33 (bottom). IL-33 activates a range of immune cells such as ILC2s, mast cells, TH2 cells (left), which leads to mucous hypersecretion, remodelling and parasite ejection (shown around the edge of the circle). H. polygyrus secretes HpARI (left hand) which binds IL-33 and DNA, tethering the cytokine within necrotic cells. H. polygyrus also secretes HpBARI (right hand) which binds and blocks ST2, the IL-33 receptor. Due to these (and other) immune modulating activities, the parasite successfully modulates the host immune response and can form chronic infections. Diagram originally conceived by Dr Francesco Vacca, and updated by Hana Pokojna.
IL-33
IL-33 is an important cytokine in a range of diseases, from parasitic infections and allergies, to colitis, metabolism and tumour immunity. Stemming for our research on how parasite modulation of the IL-33 pathway affects resistance/susceptibility, another focus of our lab is on how IL-33 responses are induced and controlled in the immune system, and how it affects responding immune cells (ILC2, mast cells, Th2 cells, stromal cells) locally and systemically.
People in my Lab
- Dr Danielle Smyth: Postdoctoral Researcher
- Dr Suzanne Hodge: Postdoctoral Researcher
- Tanya Frangova: Technician
- Josh Richards: PhD Student
- Nicole Ong: PhD Student
- Samuele Di Carmine: PhD Student
Selected Publications
- Jamwal A, Colomb F, McSorley HJ*, Higgins MK*. Structural basis for IL-33 recognition and its antagonism by the helminth effector protein HpARI2. Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 19;15(1):5226. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49550-0.
- Colomb F, Ogunkanbi A, Jamwal A, Dong B, Maizels RM, Finney CAM, Wasmuth JD, Higgins MK, McSorley HJ. IL-33-binding HpARI family homologues with divergent effects in suppressing or enhancing type 2 immune responses. Infect Immun. 2024 Mar 12;92(3):e0039523. doi: 10.1128/iai.00395-23.
- McSorley HJ, Smyth DJ. IL-33: A central cytokine in helminth infections. Semin Immunol. 2021 Mar;53:101532. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2021.101532. Epub 2021 Nov 22. PMID: 34823996.
- Vacca F, Chauché C, Jamwal A, Hinchy EC, Heieis G, Webster H, Ogunkanbi A, Sekne Z, Gregory WF, Wear M, Perona-Wright G, Higgins MK, Nys JA, Cohen ES, McSorley HJ. A helminth-derived suppressor of ST2 blocks allergic responses. Elife. 2020 May 18;9:e54017. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54017.
- Maizels RM, Smits HH, McSorley HJ. Modulation of Host Immunity by Helminths: The Expanding Repertoire of Parasite Effector Molecules. Immunity. 2018 Nov 20;49(5):801-818. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.10.016.
- Johnston CJC, Smyth DJ, Kodali RB, White MPJ, Harcus Y, Filbey KJ, Hewitson JP, Hinck CS, Ivens A, Kemter AM, Kildemoes AO, Le Bihan T, Soares DC, Anderton SM, Brenn T, Wigmore SJ, Woodcock HV, Chambers RC, Hinck AP, McSorley HJ, Maizels RM. A structurally distinct TGF-β mimic from an intestinal helminth parasite potently induces regulatory T cells. Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 23;8(1):1741. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01886-6. PMID: 29170498; PMCID: PMC5701006.
- Osbourn M, Soares DC, Vacca F, Cohen ES, Scott IC, Gregory WF, Smyth DJ, Toivakka M, Kemter AM, le Bihan T, Wear M, Hoving D, Filbey KJ, Hewitson JP, Henderson H, Gonzàlez-Cìscar A, Errington C, Vermeren S, Astier AL, Wallace WA, Schwarze J, Ivens AC, Maizels RM, McSorley HJ. HpARI Protein Secreted by a Helminth Parasite Suppresses Interleukin-33. Immunity. 2017 Oct 17;47(4):739-751.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.015.
- McSorley HJ, Blair NF, Smith KA, McKenzie AN, Maizels RM. Blockade of IL-33 release and suppression of type 2 innate lymphoid cell responses by helminth secreted products in airway allergy. Mucosal Immunol. 2014 Sep;7(5):1068-78. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.123. Epub 2014 Feb 5. PMID: 24496315; PMCID: PMC4016792.
Teaching
Henry is course lead and teaches on the the BS32009 Immunology 3rd year, and the BS42006 Advanced Immunology 4th year undergraduate modules.
Media availability
I am available for media commentary on my research.
Immunological interactions with helminth parasites
Contact Corporate Communications for media enquiries.
Areas of expertise
- Asthma and allergies
- Immunology
- Infectious diseases
PhD Projects
Principal supervisor
Awards
| Award | Year |
|---|---|
| Major Personal Funding Awards / Wellcome Investigator Award | 2021 |
Stories
Press release
University of Dundee experts have made a crucial scientific breakthrough that could herald the development of vaccines against parasitic worms.

News
We have a bumper crop of promotions this year as part of the 2022 Annual Review process for academic staff.
Press release
A University of Dundee researcher has been awarded £1.6 million in funding to further his research into immune responses, which may produce insights into a variety of diseases, including asthma, obesity, and parasitic infections.
